如何在 ASP.NET Core 中实现中间件管道
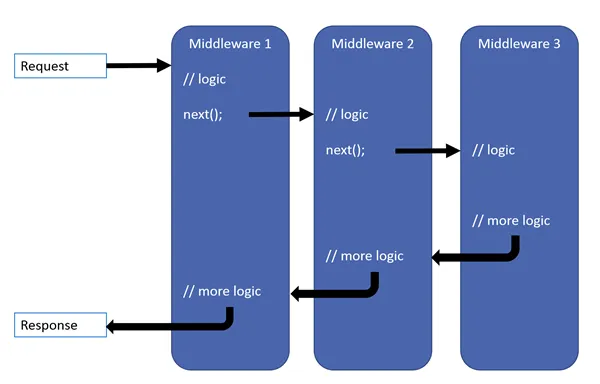
借助 ASP.NET Core,中间件流水线可以作为一种轻量级、灵活的机制,使开发人员能够在请求流水线的不同阶段插入功能。这些中间件组件可以执行各种任务,例如日志记录、身份验证、授权、异常处理等。它们提供了一种封装和组织代码的方法,促进了更简洁、更易于维护的应用程序架构。
什么是 ASP.NET Core 中的中间件?
ASP.NET Core 中的中间件是指拦截 HTTP 请求和响应的组件。它位于服务器和应用程序之间,允许您处理请求、执行逻辑和生成响应。
将中间件想象成 Web 服务器和应用程序之间的友好看门人。这就像俱乐部的保镖,决定谁进去,谁不进去。
ASP.NET Core Pipeline 中中间件的功能
中间件在请求处理管道中运行,其中每个中间件组件在将传入请求传递给下一个组件之前处理传入请求。这允许请求处理逻辑的模块化和定制。
ASP.NET Core 中的中间件类型
ASP.NET Core 中的中间件主要有两种风格:
- 内置中间件
- 自定义中间件
中间件剖析
ASP.NET Core 中的请求处理管道充当处理传入 HTTP 请求和生成适当响应的主干。把它想象成工厂中一条组织良好的装配线,其中每个工作站(中间件组件)执行一项特定任务来处理请求,然后再将其传递给下一个工作站。
流水线的核心是文件,我们在其中配置中间件组件以形成流水线。让我们看一下该文件的简化版本:Startup.csStartup.cs
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// Configure services here
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
// Configure middleware pipeline here
// Example: Logging Middleware
app.UseMiddleware<LoggingMiddleware>();
// Example: Authentication Middleware
app.UseAuthentication();
// Example: Routing Middleware
app.UseRouting();
// Example: Authorization Middleware
app.UseAuthorization();
// Example: Endpoint Middleware
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
}
}
中间件组件在管道中的排列方式
中间件组件将添加到文件方法中的管道中。这些组件的添加顺序决定了它们的执行顺序。此顺序至关重要,因为它决定了如何处理请求和生成响应。ConfigureStartup.cs
在文件中,中间件组件是使用 ASP.NET Core 提供的扩展方法添加的,例如 、 、 等。让我们看看中间件组件在方法中是如何排列的:Startup.csUseMiddlewareUseAuthenticationUseRoutingConfigure
// Configure method in Startup.cs
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
// Configure middleware pipeline here
// Example: Logging Middleware
app.UseMiddleware<LoggingMiddleware>();
// Example: Authentication Middleware
app.UseAuthentication();
// Example: Routing Middleware
app.UseRouting();
// Example: Authorization Middleware
app.UseAuthorization();
// Example: Endpoint Middleware
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
}
中间件的执行顺序
将中间件组件添加到方法中的顺序与其执行顺序相对应。中间件组件按顺序执行,每个组件处理请求并将其传递给管道中的下一个组件。Configure
例如,在上面的代码片段中,将在 之前执行,而 将在 之前执行,依此类推。这种顺序执行允许每个中间件组件根据需要检查、修改或短路请求处理。LoggingMiddlewareAuthenticationMiddlewareRoutingMiddleware
中间件如何与传入请求和传出响应进行交互
中间件组件通过在传入请求和传出响应通过管道时拦截它们来与它们进行交互。中间件可以检查、修改甚至短路请求处理,允许开发人员为日志记录、身份验证和授权等任务添加自定义逻辑。
让我们举个例子:LoggingMiddleware
// LoggingMiddleware.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class LoggingMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public LoggingMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// Log request details
Console.WriteLine($"Request: {context.Request.Path}");
// Call the next middleware in the pipeline
await _next(context);
// Log response details
Console.WriteLine($"Response: {context.Response.StatusCode}");
}
}
在此中间件中,我们拦截传入的请求,记录其详细信息,然后使用委托将其传递给管道中的下一个中间件。同样,我们可以拦截传出响应,记录其详细信息,并继续处理请求。_next
构建自定义中间件
ASP.NET Core 中的自定义中间件使开发人员能够将定制功能直接注入请求处理管道中。通过创建和实现中间件类,可以自定义应用程序处理传入请求和传出响应的方式。下面是自定义中间件类的示例:
// CustomMiddleware.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class CustomMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public CustomMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// Custom logic before the next middleware
await _next(context); // Call the next middleware in the pipeline
// Custom logic after the next middleware
}
}
创建自定义中间件涉及使用遵循签名的方法实现类。在此方法中,可以定义要在调用管道中的下一个中间件之前和之后执行的自定义逻辑。这将封装要注入到请求处理流中的特定功能。InvokeAsyncRequestDelegate
处理请求和响应
ASP.NET Core 中的中间件组件提供对传入请求和传出响应的精细控制。在自定义中间件中,您可以访问和操作请求和响应对象,以根据应用程序的要求定制其行为。下面介绍如何在自定义中间件中处理请求和响应:
// CustomMiddleware.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class CustomMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public CustomMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// Handle incoming request
// Custom logic to inspect, modify, or validate the request
await _next(context); // Call the next middleware in the pipeline
// Handle outgoing response
// Custom logic to inspect or modify the response before it's sent back to the client
}
}
解释:
在自定义中间件的方法中,您可以访问传入和传出对象。这允许您通过执行检查、修改、验证等任务来处理请求,同样,在将响应发送回客户端之前处理响应。这为在请求处理管道中实现自定义行为提供了一种灵活的机制。InvokeAsyncHttpContext.RequestHttpContext.Response
注册自定义中间件
若要将自定义中间件集成到 ASP.NET Core 应用程序中,需要在中间件管道中注册它。这涉及将自定义中间件类添加到文件中的管道配置中。以下是注册自定义中间件的方法:Startup.cs
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
// Register custom middleware in the pipeline
app.UseMiddleware<CustomMiddleware>();
// Other middleware registrations...
}
}
若要将自定义中间件合并到中间件管道中,需要在文件的方法中注册它。在这里,该方法用于将自定义中间件类 ( ) 添加到管道中。确保注册顺序与管道中所需的执行顺序一致。ConfigureStartup.csUseMiddlewareCustomMiddleware
使用内置中间件
ASP.NET Core 中的内置中间件提供了开箱即用的基本功能,使开发人员能够简化 Web 应用程序中的常见任务。这些中间件组件处理请求处理管道的各个方面,例如提供静态文件、身份验证和路由。我们来探讨一些常用的内置中间件:
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseStaticFiles(); // Serve static files like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
app.UseAuthentication(); // Enable authentication middleware
app.UseRouting(); // Enable routing middleware
}
}
在此代码片段中,我们将在文件的方法中配置内置中间件组件。ConfigureStartup.cs
- app.UseStaticFiles():此中间件用于将 HTML、CSS、JavaScript 和图像等静态文件直接提供给客户端,而无需额外的服务器端处理。它使应用程序能够有效地提供静态内容。
- app.UseAuthentication():此中间件为应用程序启用身份验证。它提供了用于对用户进行身份验证并根据用户身份授权访问资源的机制。身份验证对于保护应用程序中的敏感终结点和数据至关重要。
- app.UseRouting():此中间件为应用程序启用路由。它定义 URL 模式并将传入的 HTTP 请求映射到相应的终结点(控制器/操作或 Razor 页面处理程序)。路由中间件对于实现 RESTful 路由和处理不同类型的请求至关重要。
如何在管道中配置内置中间件
在 ASP.NET Core 管道中配置内置中间件非常简单,涉及将中间件组件添加到文件中。通过按正确的顺序注册这些中间件组件,可以确保它们在请求处理流的适当阶段执行。让我们看看如何配置内置中间件:Startup.cs
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
// Configure built-in middleware components
app.UseStaticFiles(); // Serve static files
app.UseAuthentication(); // Enable authentication
app.UseRouting(); // Enable routing
}
}
与前面的代码片段类似,此代码在文件的方法中配置内置中间件组件。ConfigureStartup.cs
内置中间件示例(静态文件、身份验证、路由)
ASP.NET Core 提供了一组丰富的内置中间件组件,可满足 Web 开发中的常见需求。内置中间件的一些示例包括:
- **静态文件中间件:**此中间件将静态文件(如 HTML、CSS、JavaScript 和图像)直接提供给客户端,而无需额外的服务器端处理。
- **身份验证中间件:**身份验证中间件有助于用户身份验证和授权,从而可以保护应用程序的终结点和资源。
- **路由中间件:**路由中间件将传入的 HTTP 请求映射到相应的控制器操作或 Razor 页面处理程序,从而在 ASP.NET Core 应用程序中实现 RESTful 路由。
让我们深入了解如何使用这些内置中间件组件的示例:
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
// Example: Serve static files
app.UseStaticFiles();
// Example: Enable authentication
app.UseAuthentication();
// Example: Enable routing
app.UseRouting();
}
}
此代码片段提供了在 ASP.NET Core 应用程序中使用常用内置中间件组件的示例。
- app.UseStaticFiles():此中间件将应用程序的 wwwroot 目录中的静态文件提供给客户端。它通常用于提供应用程序客户端部分所需的 CSS、JavaScript、图像和其他静态资源。
- app.UseAuthentication():此中间件在应用程序中启用身份验证,允许用户登录并访问受保护的资源。它设置用户身份验证所需的身份验证服务和中间件组件。
- app.UseRouting():此中间件为应用程序设置路由,使其能够根据 URL 模式将传入的 HTTP 请求与相应的控制器操作或 Razor 页面处理程序进行匹配。路由对于定义应用程序的终结点和 API 路由至关重要。
中间件流水线配置
在Startup.cs中设置
在 ASP.NET Core 中配置中间件管道是应用程序设置的一个关键方面,它允许开发人员定义如何处理和处理 HTTP 请求。下面介绍如何在文件中设置中间件管道:Startup.cs
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseMiddleware<LoggingMiddleware>(); // Adding custom middleware to the pipeline
app.UseAuthentication(); // Enabling authentication middleware
app.UseRouting(); // Enabling routing middleware
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers(); // Mapping controllers for endpoint routing
});
}
}
在文件的方法中,通过添加各种中间件组件来配置中间件管道。ConfigureStartup.cs
- app.UseMiddleware<LoggingMiddleware>():将自定义日志记录中间件添加到管道,允许自定义记录传入请求和传出响应。
- app.UseAuthentication():启用身份验证中间件以处理用户身份验证和授权。
- app.UseRouting():启用路由中间件,该中间件负责将传入请求映射到相应的端点。
- app.UseEndpoints():配置终结点路由以将 HTTP 请求映射到控制器操作或 Razor 页面。
重新排序和条件执行
对中间件进行重新排序并有条件地执行它们可能会显著影响请求处理流和应用程序行为。下面介绍如何重新排序和有条件地执行文件中的中间件:Startup.cs
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseAuthentication(); // Enabling authentication middleware
app.UseMiddleware<CustomMiddleware>(); // Adding custom middleware to the pipeline
app.UseRouting(); // Enabling routing middleware
app.UseStaticFiles(); // Serving static files
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers(); // Mapping controllers for endpoint routing
});
}
}
可以在方法中对中间件组件重新排序,以更改其在管道中的执行顺序。Configure
- 在此示例中,身份验证中间件 () 位于自定义中间件 () 之前。这可确保在中间件中的任何自定义逻辑之前执行身份验证。app.UseAuthentication()app.UseMiddleware<CustomMiddleware>()
- 静态文件中间件 () 位于路由中间件 () 之后,表示在提供静态文件之前应解析路由。app.UseStaticFiles()app.UseRouting()
安全中间件
身份验证和授权是确保资源的机密性、完整性和可用性的基本方面。让我们深入探讨 ASP.NET Core 中安全中间件的重要性和概述:
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseAuthentication(); // Enable authentication middleware
app.UseAuthorization(); // Enable authorization middleware
// Other middleware configurations...
}
}
说明:
在文件中,用于身份验证和授权的中间件组件分别使用 和 方法添加到应用程序管道中。这可确保传入请求在应用程序进一步处理之前经过身份验证和授权。身份验证验证用户的身份,而授权则根据预定义的策略控制他们对资源的访问。通过整合这些中间件组件,开发人员可以在整个应用程序中一致地实施安全措施,保护其免受未经授权的访问和恶意攻击。Startup.csUseAuthentication()UseAuthorization()
用于安全的自定义中间件
自定义安全中间件使开发人员能够实施符合其应用程序要求的定制安全措施。通过创建自定义中间件,开发人员可以强制执行其他安全检查、日志记录或其他与安全相关的功能。让我们来探讨一下自定义中间件如何增强 ASP.NET Core 中的安全性:
// CustomSecurityMiddleware.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class CustomSecurityMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public CustomSecurityMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// Custom security logic before proceeding to the next middleware
// Example: Additional security checks, logging, etc.
await _next(context); // Proceed to the next middleware
}
}
在startup.cs:
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseMiddleware<CustomSecurityMiddleware>(); // Add custom security middleware
// Other middleware configurations...
}
}
解释:
该类通过定义一个方法来实现自定义安全中间件,该方法采用一个参数。在此方法中,开发人员可以实现自定义安全逻辑,例如额外的安全检查或日志记录,然后再继续管道中的下一个中间件。在文件中,该方法用于将此自定义中间件添加到应用程序管道中。这使开发人员能够根据其应用程序的特定要求定制安全措施,从而增强其整体安全态势。CustomSecurityMiddlewareInvokeAsyncHttpContextStartup.csUseMiddleware<CustomSecurityMiddleware>()
使用中间件实现端点安全
中间件在保护应用程序端点方面发挥着重要作用,它通过拦截传入请求并在将请求路由到适当的控制器或操作之前应用安全措施。让我们来探讨一下中间件如何促进 ASP.NET Core 中的端点安全:
// EndpointSecurityMiddleware.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class EndpointSecurityMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public EndpointSecurityMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// Endpoint security logic before routing to controllers or actions
// Example: Authentication, authorization, request validation, etc.
await _next(context); // Proceed to route the request
}
}
在Startup.cs:
// Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseMiddleware<EndpointSecurityMiddleware>(); // Add endpoint security middleware
// Other middleware configurations...
}
}
该类实现中间件,通过在传入请求路由到控制器或操作之前截获传入请求来保护应用程序终结点。与自定义安全中间件类似,开发人员可以在方法中实现特定于端点的安全逻辑,以对用户进行身份验证、授权访问或执行请求验证。在文件中,该方法将此终结点安全中间件添加到应用程序管道,确保在所有终结点上一致地强制执行安全措施。这有助于保护应用程序免受未经授权的访问和潜在的安全威胁。