C#数据结构 — 二叉树

二叉树是由节点组成的分层数据结构,每个节点最多可以有两个子节点,通常称为左子节点和右子节点。在本文中,我将探讨二叉树的基本概念,并使用 .NET 中的代码示例演示主要的遍历策略。
二叉树
以下是与二叉树相关的一些重要术语:
- **节点:**它表示树中的终止点。
- 根节点:它是二叉树的顶部节点。
- 分支:指树结构中节点之间的连接或路径,表示父节点与其子节点之间的关系。它还使用术语“根分支”来表示树的最顶端节点,“左分支”用于将父节点连接到其左侧子节点的分支,“右分支”用于将父节点连接到其右侧子节点的分支。
- **父节点:**它是树中至少有一个节点的节点(根除外)。
- 子节点:是连接到其上方节点的节点。
- 叶节点:是一个没有子节点的节点,位于树的底层。
- **内部节点:**它是至少有一个子节点的节点。
- **深度:**从根节点到该节点的最长路径上的边数。
- 高度:从根节点到叶节点的最长路径长度。
节点
在二叉树中,节点是表示树中单个数据元素的块。每个节点包含两个主要组件:
- 数据:可以是任何类型(即:整数、字符串、对象等)。
- 对子项的引用:二叉树中的每个节点最多可以有两个子项:一个左子节点和一个右子节点。节点通过这些引用相互连接,形成二叉树的层次结构。
二叉树具有以下三个特征:
- 只有一个根。
- 每个节点最多有两个子节点。
- 根和任何节点之间只有一条路径(连接)。
二叉树示例
下面您可以看到二叉树的图形表示。这是二叉树的一个示例,但树可能更大或更小:
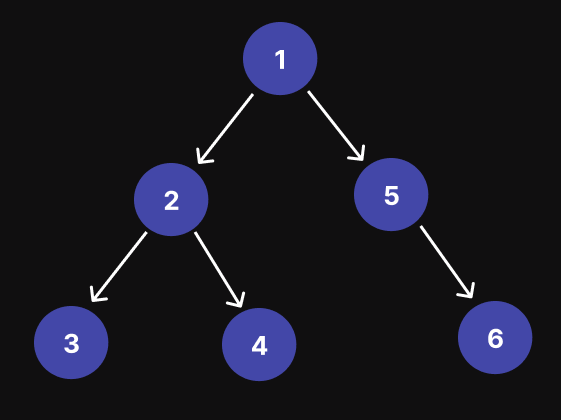
- 节点 1 是根节点。
- 节点 1 包含 2 个子节点:节点 2(左节点)和节点 5(右节点)。
- 节点 2 包含两个子节点:节点 3(左节点)和节点 4(右节点)。
- 节点 5 仅包含一个子节点:节点 6(右节点)。
- 节点 3、4 和 6 是叶节点。
树节点
这是 C# 中一个类的表示形式:TreeNode
public class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val = 0, TreeNode left = null, TreeNode right = null) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
出于演示目的,我将创建以下二叉树,它将在下一个示例中使用:
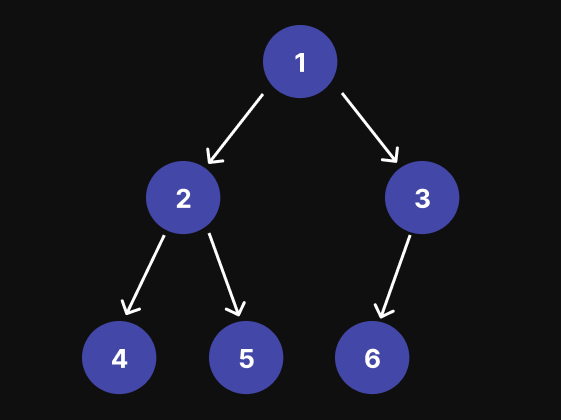
// Tree with nodes \[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, null\]
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ /
// 4 5 6
static TreeNode CreateDemoTree()
{
return new TreeNode(1)
{
left = new TreeNode(2)
{
left = new TreeNode(4),
right = new TreeNode(5)
},
right = new TreeNode(3)
{
left = new TreeNode(6)
}
};
}
通过这个类,现在让我们深入了解如何迭代二叉树。
树遍历算法
遍历策略是一种方法或技术,用于按特定顺序访问数据结构(如树或图形)中的所有节点。在二叉树的上下文中,遍历策略决定了访问和处理节点的顺序。遍历策略对于各种应用程序至关重要,包括数据搜索、操作和结构验证。
有两种通用策略可用于遍历树:
- **深度优先搜索(DFS):**在这种策略中,我们采用优先顺序,以便从根部开始,一直到某个叶子,然后回到根部到达另一个分支。DFS 可用于执行 、 和 遍历。DFS 使用堆栈数据结构(通过递归显式或隐式)来跟踪访问的节点和遍历顺序。depthPreorderInorderPostorder
- **广度优先搜索 (BFS):**在此策略中,我们按照高度顺序从上到下逐级扫描树。较高级别的节点将在较低级别的节点之前访问。此策略在移动到下一级节点之前探索节点的所有邻居。BFS 可用于执行和遍历。BFS 使用队列来维护要访问的节点的顺序。Level OrderReverse Level Order
如果你想知道堆栈或队列是如何工作的,请查看我的文章:
- 数据结构 — 堆栈
- 数据结构 — 队列
用于探索和处理二叉树节点的五种常用方法是:
- 预顺序遍历: 按以下顺序遍历整个二叉树:.Root -> Left -> Right
- Inorder Traversal: 按以下顺序遍历整个二叉树: .Left -> Root -> Right
- Postorder Traversal: 按以下顺序遍历整个二叉树: .Left -> Right -> Root
- 关卡顺序遍历: 逐级遍历每个关卡的整个二叉树,从来往,逐个关卡。Top to BottomLeft -> Right
- 反向级别顺序遍历: 在每个级别遍历整个二叉树(以相反的顺序存储结果)。Bottom to TopRight -> Left
执行树遍历的三种常见方法是:
- 递归方法:在这种方法中,我们使用递归来执行遍历。为此,我们创建了一个辅助函数来递归遍历二叉树。它初始化一个空列表来存储遍历的结果,然后调用帮助程序函数,将二叉树的根和结果列表作为参数传递。
- 使用堆栈遍历树:在这种方法中,堆栈用于模拟递归过程并迭代遍历二叉树。它初始化一个空列表来存储遍历的结果,并初始化一个堆栈来跟踪需要处理的节点。
- Morris 遍历方法:在这种方法中,我们通过在二叉树中建立和删除临时链接来遍历树,而无需使用堆栈或递归。
接下来,我将介绍这些方法中的每一种。
预购遍历 (DFS)
预序遍历是一种树遍历算法,用于系统地访问二叉树中的每个节点。它之所以获得此名称,是因为根节点在其子节点之前被访问。在这种方法中,您将按照“根 -> 左 -> 右”的顺序遍历整个二叉树。
按以下顺序访问节点:
- 首先,访问树的根节点并处理其值。
- 然后访问左子树(移动到当前节点的左子树)。
- 然后访问右子树(在访问左子树中的所有节点之后)
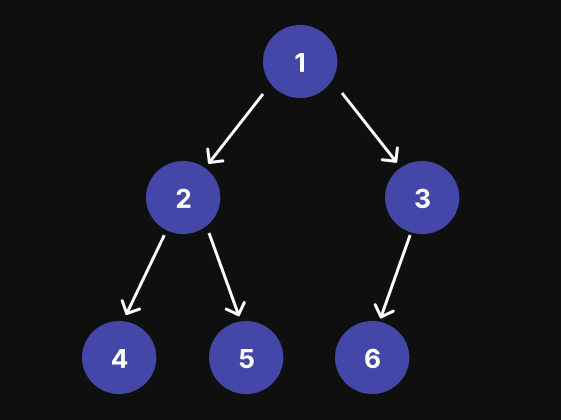
例如,对于下图中的二进制三,预序遍历的结果为:[1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6]
递归方法
在预序遍历的递归方法中,我们从根节点开始访问每个节点,然后递归访问左侧子树,最后递归访问右侧子树:
public static IList<int> RecursiveApproach(TreeNode root)
{
List<int> result = new List<int>();
// Call the helper function to perform the preorder traversal recursively
Preorder(root, result);
return result;
}
// Helper method that performs the traversal
private static void Preorder(TreeNode node, List<int> result)
{
if (node == null) return;
// Visit the current node (root) and add its value to the result list
result.Add(node.val);
// Recursively traverse the left subtree
Preorder(node.left, result);
// Recursively traverse the right subtree
Preorder(node.right, result);
}
使用堆栈的迭代方法
在这种方法中,我们从根开始,然后在每次迭代时,将当前节点从堆栈中弹出并访问此节点。然后,如果这个节点有一个右边的子节点,我们把它的右边的子节点推入堆栈中,如果这个节点有一个左边的子节点,我们把它的左边子节点推到堆栈中(我们先推右边的子节点,这样我们就可以先访问左边的子节点,因为堆栈的性质是后进先出 — 后进先出), 之后,我们可以继续下一次迭代,直到堆栈为空。在这种方法中,我们按照 Top-Bottom 和 Left -> Right 的顺序将节点推送到输出列表中,这自然地再现了预序遍历:
public static IList<int> IterativeApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a stack to store nodes that need to be processed
var stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
// Initialize a list to store the preorder traversal result
var output = new List<int>();
if (root == null)
{
return output;
}
stack.Push(root);
while (stack.Count > 0)
{
// Get the current element in the stack
TreeNode node = stack.Pop();
// Add the value of the popped node to the output list
output.Add(node.val);
// If the popped node has a right child, push it onto the stack
if (node.right != null)
{
stack.Push(node.right);
}
// If the popped node has a left child, push it onto the stack
if (node.left != null)
{
stack.Push(node.left);
}
}
// Return the output list containing the preorder traversal of the tree
return output;
}
Morris 遍历方法
在此方法中,遍历从根节点开始,并遵循以下步骤:对于每个节点,如果它没有左子节点,则将其值添加到输出中,然后继续到右子节点。如果节点具有左侧子节点,则它会在左侧子树(前置节点)中找到最右边的节点。如果前置节点的右侧子节点为 null,则算法将创建一个返回当前节点的伪链接,并移动到左侧子节点。如果前置节点已指向当前节点,则删除链接,并将遍历移动到正确的子节点。此方法有效地按顺序遍历树,同时避免额外的内存使用,伪链接用作导航的临时痕迹导航。
public static IList<int> MorrisTraversalApproach(TreeNode root)
{
var output = new List<int>();
TreeNode node = root;
// Traverse the tree until we reach the end
while (node != null)
{
// If the current node has no left child
if (node.left == null)
{
// Add the value of the current node to the output list
output.Add(node.val);
// Move to the right child of the current node
node = node.right;
}
else
{
// If the current node has a left child
// Find the predecessor of the current node
TreeNode predecessor = node.left;
while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != node)
{
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
// If the predecessor's right child is null, link it to the current node and move to the left child
if (predecessor.right == null)
{
// Add the value of the current node to the output list
output.Add(node.val);
// Link the predecessor's right child to the current node
predecessor.right = node;
// Move to the left child
node = node.left;
}
else
{
// If the predecessor's right child is not null, unlink it and move to the right child
// Unlink the predecessor's right child
predecessor.right = null;
// Move to the right child
node = node.right;
}
}
}
// Return the preorder traversal output
return output;
}
无序遍历 (DFS)
Inorder 遍历是一种树遍历算法,用于系统地访问二叉树中的每个节点。在这种方法中,您将按照“左-根-右”的顺序遍历整个二叉树。
按以下顺序访问节点:
- 首先,访问左子树,从根节点开始,移动到当前节点的左侧子节点(如果存在)。重复此过程,直到到达没有左子节点的节点。
- 然后访问右子树,移动到其右侧子树(如果存在)。对正确的子树重复遍历过程。
- 然后对二叉树中的每个节点重复这些步骤,直到访问完所有节点。
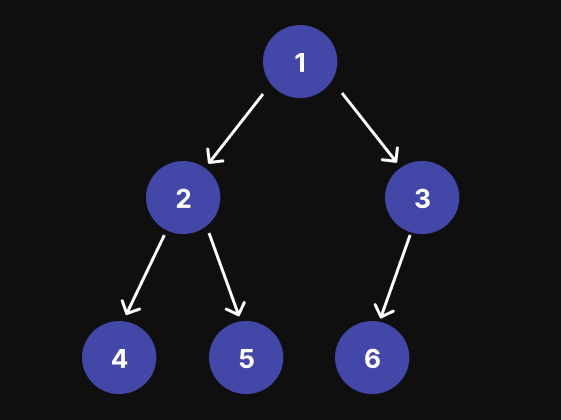
总之,我们首先访问左侧子树,然后是根节点,然后是右侧子树。例如,对于下图中的二进制三,无序遍历的结果为:[4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3]
递归方法
在无序遍历的递归方法中,我们首先检查当前节点是否不为 null,如果为 null,则递归遍历左侧子树,将当前节点的值添加到输出列表中,然后递归遍历右侧子树。
此过程一直持续到访问二叉树中的所有节点为止。因此,该列表包含按排序顺序排列的二叉树元素,表示无序遍历。result
public static IList<int> RecursiveApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a list to store the inorder traversal result
var result = new List<int>();
// Call the helper function to perform the inorder traversal recursively
Inorder(root, result);
// Return the list containing the inorder traversal result
return result;
}
// Helper method that performs the traversal
private static void Inorder(TreeNode root, List<int> output)
{
// Base case: If the current node is not null
if (root != null)
{
// Traverse the left subtree of the current node recursively
Inorder(root.left, output);
// Add the value of the current node to the output list
output.Add(root.val);
// Traverse the right subtree of the current node recursively
Inorder(root.right, output);
}
}
使用堆栈的迭代方法
在这种方法中,我们从设置为二叉树根的当前节点开始,代码进入一个循环,该循环一直持续到当前节点变为 null 并且堆栈变为空,表明所有节点都已处理完毕。
在循环中,它通过反复将每个节点推到堆栈上并移动到其左侧子节点来遍历当前节点的左侧子树。完成左侧子树遍历后,它会从堆栈中弹出一个节点,将其值添加到结果列表中,然后移动到其右侧子节点以继续无序遍历。最后,在完成遍历后,代码返回包含无序遍历结果的列表。
public static IList<int> IterativeApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a list to store the inorder traversal result
List<int> result = new List<int>();
// Initialize a stack to store nodes that need to be processed
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
// Start with the current node set to the root of the binary tree
TreeNode curr = root;
// Continue the loop until either the current node becomes null
// and the stack becomes empty, indicating that all nodes have been processed
while (curr != null || stack.Count > 0)
{
// Traverse the left subtree of the current node
while (curr != null)
{
// Push each node onto the stack
stack.Push(curr);
// Move to the left child node
curr = curr.left;
}
// Once the left subtree traversal is complete, pop a node from the stack
// This node will be the current node whose value needs to be added to the result list
curr = stack.Pop();
// Add the value of the current node to the result list
result.Add(curr.val);
// Move to the right child node to continue the inorder traversal
curr = curr.right;
}
// Once the traversal is complete, return the list containing the inorder traversal result
return result;
}
Morris 遍历方法
在这种方法中,我们初始化一个空列表来存储无序遍历结果,并将当前节点指针设置为二叉树的根。在持续到当前节点变为 null 的循环中,代码检查当前节点是否具有左子节点。如果是这样,它将在左侧子树(前置节点)中找到最右边的节点,并使当前节点成为前置节点的右子节点。rescurr
然后,它存储当前节点,移动到其左侧子节点,并将原始当前节点的左侧子节点设置为 null 以防止无限循环。如果当前节点没有左子节点,则其值将添加到结果列表中,并且当前节点将移动到其右子节点。最后,在完成遍历后,代码返回包含无序遍历结果的列表。
public static IList<int> MorrisTraversalApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a list to store the inorder traversal result
List<int> result = new List<int>();
// Initialize the current node pointer to the root of the binary tree
TreeNode curr = root;
// Initialize a pointer to keep track of the predecessor node
TreeNode pre;
// Continue the loop until the current node becomes null
while (curr != null)
{
// If the current node has no left child
if (curr.left == null)
{
// Add the value of the current node to the result list
result.Add(curr.val);
// Move to the next right node
curr = curr.right;
}
else
{
// If the current node has a left subtree
// Find the rightmost node in the left subtree (predecessor node)
pre = curr.left;
while (pre.right != null)
{
// Traverse to the rightmost node
pre = pre.right;
}
// Make the current node the right child of the predecessor node
pre.right = curr;
// Store the current node before moving to its left child
TreeNode temp = curr;
// Move the current node to the top of the new subtree
curr = curr.left;
// Set the left child of the original current node to null
// This prevents infinite loops when traversing the subtree
temp.left = null;
}
}
// Return the list containing the inorder traversal result
return result;
}
后订单遍历 (DFS)
后顺序遍历是一种树遍历算法,用于系统地访问二叉树中的每个节点。在这种方法中,您将按照“左-右-根”的顺序遍历整个二叉树。
按以下顺序访问节点:
- 首先,访问左子树。
- 然后访问右子树。
- 然后访问根节点。
这意味着对于每个节点,我们首先遍历其左子树,然后遍历其右子树,最后访问节点本身。总之,后订单遍历以自下而上的方式访问节点,从叶子开始,向根部移动。例如,对于下图中的二进制三,后序遍历的结果为:[4, 5, 2, 6, 3, 1]
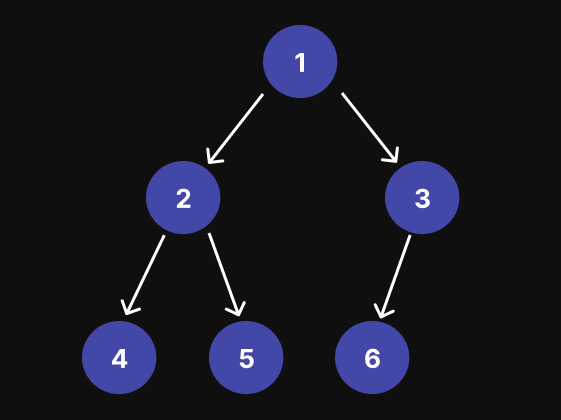
递归方法
在后序遍历的递归方法中,我们递归遍历每个节点的左子树,然后递归遍历其右子树,最后访问当前节点,从而产生后序遍历序列:
public static IList<int> RecursiveApproach(TreeNode root)
{
List<int> result = new List<int>();
Postorder(root, result);
return result;
}
// Helper method that performs the traversal
private static void Postorder(TreeNode root, List<int> result)
{
if (root == null) return;
// Traverse the left subtree
Postorder(root.left, result);
// Traverse the right subtree
Postorder(root.right, result);
// Visit the current node
result.Add(root.val);
}
使用堆栈的迭代方法
在这种方法中,我们从节点开始,将节点推到堆栈上,然后继续遍历,直到堆栈为空。root
在遍历过程中,我们从堆栈中弹出节点,在结果列表的开头插入它们的值以实现后序遍历的相反顺序,然后将它们的右子节点推到堆栈上,然后是它们的左子节点。这可确保在左子树之前处理右子树,从而迭代复制后序遍历序列。
请注意,我们在结果列表 () 的开头插入当前节点的值,这样做是为了实现后序遍历的相反顺序。
public static IList<int> IterativeApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a list to store the result of the postorder traversal
List<int> result = new List<int>();
// Initialize a stack to perform iterative traversal
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
// If the root is null, return the empty result list
if (root == null) return result;
// Push the root node onto the stack to start traversal
stack.Push(root);
// Continue traversal while the stack is not empty
while (stack.Count > 0)
{
// Pop the top node from the stack
TreeNode node = stack.Pop();
// Insert the value of the current node at the beginning of the result list
// This is done to achieve the reverse order of postorder traversal
result.Insert(0, node.val); // Insert at the beginning for postorder traversal
// Push the right child onto the stack first (if exists)
// This ensures that the right subtree is processed before the left subtree
if (node.left != null)
{
stack.Push(node.left);
}
// Push the left child onto the stack (if exists)
if (node.right != null)
{
stack.Push(node.right);
}
}
return result;
}
Morris 遍历方法
在这种方法中,我们从根节点开始,反复遍历树,直到当前节点变为 null。在遍历过程中,如果当前节点没有右子节点,我们通过将其值添加到输出列表并移动到其左子节点来处理它。如果当前节点有一个右子节点,我们找到它的无序后继节点,即其右子树的最左边节点。如果继任者的左子节点为 null,则将其链接到当前节点并移动到右侧子节点,这表明我们尚未访问右侧子树。如果继任者的左子项不为 null,则我们将其取消链接并移动到左子项,表明我们已经访问了右子树。
遍历后,我们反转输出列表以获得后序遍历序列。
public static IList<int> MorrisTraversalApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// Create a list to store the postorder traversal result
var output = new List<int>();
// Initialize the current node as the root of the tree
TreeNode node = root;
// Traverse the tree until the current node is not null
while (node != null)
{
if (node.right == null)
{
// If the current node has no right child, process the current node
// Add the value of the current node to the output list
output.Add(node.val);
// Move to the left child of the current node
node = node.left;
}
else
{
// If the current node has a right child
// Find the inorder successor of the current node
TreeNode successor = node.right;
while (successor.left != null && successor.left != node)
{
// Traverse to the leftmost node of the right subtree
successor = successor.left;
}
if (successor.left == null)
{
// If the successor's left child is null, link it to the current node and move to the right child
// This indicates that we haven't visited the right subtree yet
successor.left = node;
// Add the value of the current node to the output list
output.Add(node.val);
// Move to the right child
node = node.right;
}
else
{
// If the successor's left child is not null, unlink it and process the current node
// This indicates that we have already visited the right subtree
successor.left = null;
// Move to the left child
node = node.left;
}
}
}
// Reverse the output to get the postorder traversal
output.Reverse();
// Return the postorder traversal result
return output;
}
级别顺序遍历 (BFS)
级别顺序遍历从左到右逐级遍历整个树。为此,我们可以使用递归或使用广度优先搜索 (BFS)。 例如,对于下图中的二进制三,级别顺序遍历的结果为:[[1], [2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
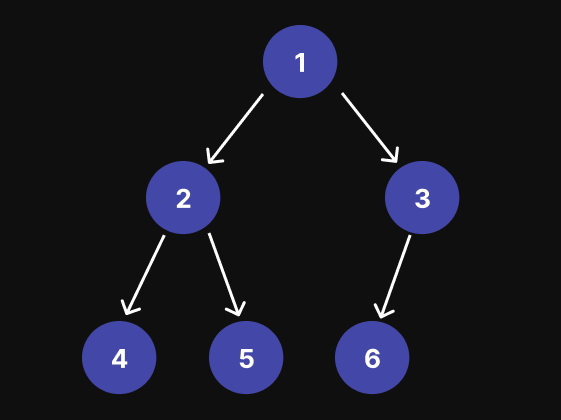
递归方法
在关卡顺序遍历的递归方法中,我们遍历整个树,跟踪当前关卡:
public static IList<IList<int>> RecursiveApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// Create a new list to store the result of the level order traversal
IList<IList<int>> result = new List<IList<int>>();
// If the root is null, return an empty list
if (root == null) return result;
// Start the recursive traversal from the root at level 0
LevelOrder(root, 0, result);
// Return the list of levels
return result;
}
// Helper method that performs the traversal
private static void LevelOrder(TreeNode node, int level, IList<IList<int>> result)
{
// If the list of levels doesn't have a list for the current level, create it
if (result.Count == level)
{
result.Add(new List<int>());
}
// Add the current node's value to the appropriate level
result[level].Add(node.val);
// Recursively traverse the left subtree, incrementing the level by 1
if (node.left != null)
{
LevelOrder(node.left, level + 1, result);
}
// Recursively traverse the right subtree, also incrementing the level by 1
if (node.right != null)
{
LevelOrder(node.right, level + 1, result);
}
}
将广度优先搜索 (BFS) 与队列结合使用的迭代方法
在这种方法中,我们在二叉树上执行 BFS(这是一种用于遍历或执行数据结构(如树或图形)搜索的技术),在每个级别中从上到下、从左到右逐级访问节点,并使用队列来管理每个级别要处理的节点:
public static IList<IList<int>> IterativeApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// List to store the result of the level order traversal
var result = new List<IList<int>>();
// If the tree is empty (root is null), return the empty result list
if (root == null)
{
return result;
}
// Queue to manage Breadth-First Search (BFS)
var queue = new Queue<TreeNode>();
queue.Enqueue(root); // Start by enqueuing the root node
// Loop to process nodes at each level
while (queue.Count > 0) // While there are nodes to process
{
// Get the current level size (number of nodes at this level)
int levelSize = queue.Count;
// Create a list to store the node values for the current level
var currentLevel = new List<int>();
// Process all nodes in the current level
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++)
{
// Dequeue the next node from the front of the queue
var currentNode = queue.Dequeue();
currentLevel.Add(currentNode.val); // Add its value to the current level
// Enqueue the left child if it exists
if (currentNode.left != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(currentNode.left);
}
// Enqueue the right child if it exists
if (currentNode.right != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(currentNode.right);
}
}
// Add the current level's node values to the result list
result.Add(currentLevel);
}
// Return the complete level order traversal as a list of lists
return result;
}
反向级顺序遍历 (BFS)
这种方法在每个级别上从叶子到根(从下到上)和从左到右遍历实体二叉树。为了实现这一点,我们可以使用递归或执行标准级别顺序遍历(使用带有队列的 BFS 方法),但以相反的顺序存储结果,要么收集级别,然后在末尾反转,要么将每个级别的结果推到列表的前面(后者更有效,避免了最后的完全反转操作)。
例如,对于下图中的二进制三,反向级顺序遍历的结果为:[[4, 5, 6], [2, 3], [1]]
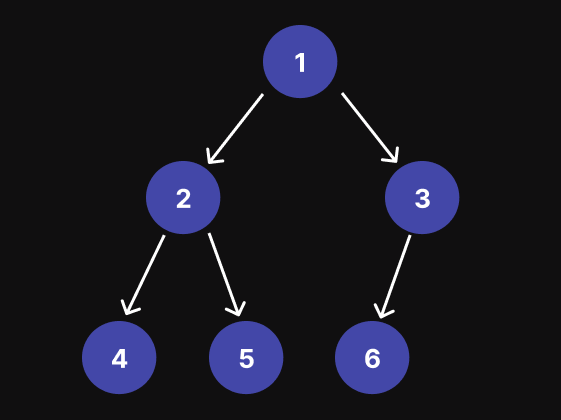
递归方法
在反向级别顺序遍历的递归方法中,我们从下到下,从左到右遍历整个树:
// The main function to perform the Reverse Level Order Traversal
public static IList<IList<int>> RecursiveApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// List to store the levels of the tree
IList<IList<int>> levels = new List<IList<int>>();
// Call the recursive helper function to populate the levels
ReverseLevelOrder(root, 0, levels);
// Create a new list to store the reversed levels
IList<IList<int>> reversedLevels = new List<IList<int>>();
// Reverse the order of the levels to achieve bottom-up traversal
for (int i = levels.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
reversedLevels.Add(levels[i]);
}
// Return the reversed levels as the result
return reversedLevels;
}
// Helper method that performs the traversal
private static void ReverseLevelOrder(TreeNode node, int level, IList<IList<int>> levels)
{
// If the node is null, return (base case)
if (node == null) return;
// If there is no list for the current level, create one
if (levels.Count <= level)
{
levels.Add(new List<int>());
}
// Add the current node's value to the list for this level
levels[level].Add(node.val);
// Recursively traverse the left subtree, incrementing the level by 1
ReverseLevelOrder(node.left, level + 1, levels);
// Recursively traverse the right subtree, incrementing the level by 1
ReverseLevelOrder(node.right, level + 1, levels);
}
将广度优先搜索 (BFS) 与队列结合使用的迭代方法
在这种方法中,我们使用队列执行 BFS 以逐级遍历树,然后反转级别的顺序以创建自下而上的结果:
public static IList<IList<int>> IterativeApproach(TreeNode root)
{
// List to store the levels of the tree
IList<IList<int>> levels = new List<IList<int>>();
if (root == null) return levels; // If the tree is empty, return empty list
// Queue to perform BFS
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new Queue<TreeNode>();
queue.Enqueue(root); // Start with the root node
// Traverse the tree level by level
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
// Get the size of the current level
int levelSize = queue.Count;
List<int> currentLevel = new List<int>();
// Process all nodes in the current level
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++)
{
// Dequeue the first node
TreeNode currentNode = queue.Dequeue();
// Add its value to the current level
currentLevel.Add(currentNode.val);
// Enqueue the left child if it exists
if (currentNode.left != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(currentNode.left);
}
// Enqueue the right child if it exists
if (currentNode.right != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(currentNode.right);
}
}
// Add the current level to the levels list
levels.Add(currentLevel);
}
// Reverse the levels to achieve bottom-up order
IList<IList<int>> reversedLevels = new List<IList<int>>();
for (int i = levels.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
reversedLevels.Add(levels[i]);
}
// Return the reversed levels as the result
return reversedLevels;
}