使用python轻松进行PDF文档处理(提取文本、表格和图像)

许多信息来自文本数据,例如在 PDF 文档中。处理 PDF 可能特别具有挑战性,尤其是对于表格和图像。
如果您使用单一模态语言模型,那么您可能已经知道它无法直接解释或“阅读”文档。它只能处理一种类型的输入,例如纯文本或纯图像。如果您需要分析 PDF 中的图像或信息图表,对于下游任务(例如问答),您通常会使用专门的软件包来解析文档。这些工具可以将文档、文档中的图像和表格转换为模型可以理解和分析的文本格式。
有几个很好的工具可用于解析下游任务的 PDF 文档。在本文中,我们将列出一些不错的功能,包括 PyPDF、Adobe PDF Services API、Camelot 和 Tabula。
首先,让我们安装相关库:
!pip install pdfservices-sdk
!pip install openpyxl
!pip install camelot-py
!pip install opencv-python
!pip install tabula-py==2.9.0
!pip install jpype1
!pip install langchain
!pip install langchain-core==0.1.40
使用 PyPDF 提取文本、表格和图像
Pypdf 是一个用于解析 PDF 文档的通用库。它可以将文档(包括文档中的表格)解析为文本。大多数时候,在使用 PyPDF 解析文档时,表格的格式也得到了很好的保留。

Langchain document_loaders包含许多不同的包来读取各种文件格式,包括PyPDF。以下脚本使用 PyPDF 处理文档,并将其保存为数据帧格式:
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
def extract_text_from_file(df, file_path):
file_name = file_path.split("/")[-1]
file_type = file_name.split(".")[-1]
if file_type == "pdf":
loader = PyPDFLoader(file_path)
else:
return df
text = ""
pages = loader.load_and_split()
for page in pages:
text += page.page_content
# Create a new df and concatenate
new_row = pd.DataFrame({"file": [file_name], "text": [text]})
df = pd.concat([df, new_row], ignore_index=True)
return df
#Apply the function:
folder_path = '../data/raw'
pathlist = Path(folder_path).glob('*.pdf')
filenames = []
for file_path in pathlist:
filename = os.path.basename(file_path)
filenames.append(filename)
df = pd.DataFrame()
for filename in filenames:
file_path = folder_path + "/" + filename
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path)
print(f"{datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')} process {file_name}")
# Initialize an empty df
df_file = pd.DataFrame(columns=["file", "text"])
print(f"{datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')} extract text")
try:
df_file = extract_text_from_file(df_file, file_path)
except Exception as e:
print("----Error: cannot extract text")
print(f"----error: {e}")
df = pd.concat([df, df_file])
df

您还可以单独处理每个页面,例如,如果您想在每个块/页面上执行下游问答任务。在这种情况下,您可以按如下方式修改脚本:
def extract_text_from_file(df, file_path):
file_name = file_path.split("/")[-1]
file_type = file_name.split(".")[-1]
if file_type == "pdf":
loader = PyPDFLoader(file_path)
elif file_type == "docx":
loader = Docx2txtLoader(file_path)
else:
return df
pages = loader.load_and_split()
for page_number, page in enumerate(pages, start=1):
# Each page's text is added as a new row in the DataFrame
new_row = pd.DataFrame({
"file": [file_name],
"page_number": [page_number],
"text": [page.page_content]
})
df = pd.concat([df, new_row], ignore_index=True)
return df

PDF 文档的每一页都可以包含任意数量的图像。您知道您还可以使用 PyPDF 从文档中提取所有图像吗?
以下代码块从pdf文件中提取所有图像,并创建一个新文件夹来存储提取的图像:
from pypdf import PdfReader
import os
output_directory = '../data/processed/images/image_pypdf'
if not os.path.exists(output_directory):
os.mkdir(output_directory)
reader = PdfReader("../data/raw/GPTsareGPTs.pdf")
for page in reader.pages:
for image in page.images:
with open(os.path.join(ouput_directory,image.name), "wb") as fp:
fp.write(image.data)
在文件夹中,您将找到 PDF 中的所有图像:
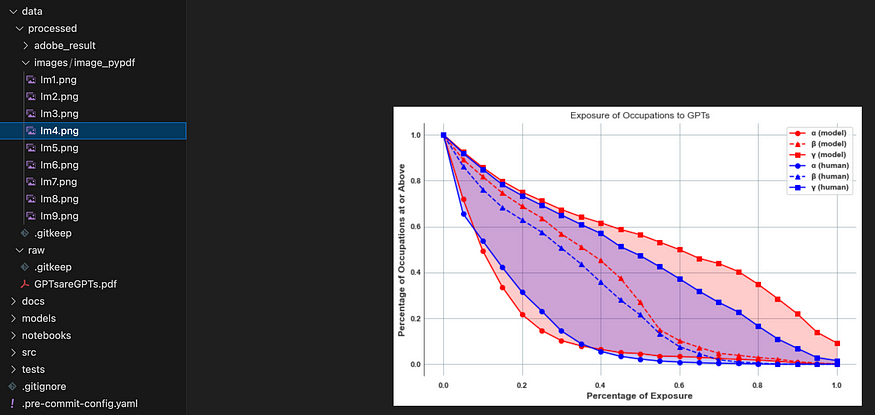
PyPDF 提取的 PDF 中所有图像的列表。图片由作者提供
使用 Adobe PDF Services API 提取文本、表格和图像
PDF 提取 API(包含在 PDF 服务 API 中)提供基于云的功能,用于自动从 PDF 中提取内容。
PDF 服务 API 需要access_token来授权请求。为了使用访问令牌,您需要创建一个。收到包含 json 格式的 client_id 和 client_secret 的开发人员凭据后,您可以使用它来处理您的 PDF。让我们先导入相关库:
from adobe.pdfservices.operation.auth.credentials import Credentials
from adobe.pdfservices.operation.exception.exceptions import ServiceApiException, ServiceUsageException, SdkException
from adobe.pdfservices.operation.execution_context import ExecutionContext
from adobe.pdfservices.operation.io.file_ref import FileRef
from adobe.pdfservices.operation.pdfops.extract_pdf_operation import ExtractPDFOperation
from adobe.pdfservices.operation.pdfops.options.extractpdf.extract_pdf_options import ExtractPDFOptions
from adobe.pdfservices.operation.pdfops.options.extractpdf.extract_element_type import ExtractElementType
from adobe.pdfservices.operation.pdfops.options.extractpdf.extract_renditions_element_type import \
ExtractRenditionsElementType
import os.path
import zipfile
import json
import pandas as pd
import re
import openpyxl
from datetime import datetime
以下脚本使用必要的凭据设置 Adobe PDF Services API,并处理 PDF 文件并将结果保存在 zip 文件中:
def adobeLoader(input_pdf, output_zip_path,client_id, client_secret):
"""
Function to run adobe API and create output zip file
"""
# Initial setup, create credentials instance.
credentials = Credentials.service_principal_credentials_builder() \
.with_client_id(client_id) \
.with_client_secret(client_secret) \
.build()
# Create an ExecutionContext using credentials and create a new operation instance.
execution_context = ExecutionContext.create(credentials)
extract_pdf_operation = ExtractPDFOperation.create_new()
# Set operation input from a source file.
source = FileRef.create_from_local_file(input_pdf)
extract_pdf_operation.set_input(source)
# Build ExtractPDF options and set them into the operation
extract_pdf_options: ExtractPDFOptions = ExtractPDFOptions.builder() \
.with_elements_to_extract([ExtractElementType.TEXT, ExtractElementType.TABLES]) \
.with_elements_to_extract_renditions([ExtractRenditionsElementType.TABLES,
ExtractRenditionsElementType.FIGURES]) \
.build()
extract_pdf_operation.set_options(extract_pdf_options)
# Execute the operation.
result: FileRef = extract_pdf_operation.execute(execution_context)
# Save result to output path
if os.path.exists(output_zip_path):
os.remove(output_zip_path)
result.save_as(output_zip_path)
此操作的输出是一个包含以下内容的sdk.zip包:adobeLoader
- structuredData.json文件
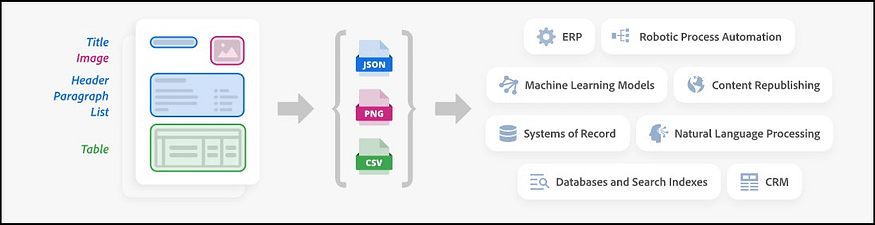
- 文本存储在 json 文件中,并在上下文块中提取 - 段落、标题、列表、脚注。
- “table”文件夹:使用为每个单元格提供的内容和表格格式信息提取和解析表格。表数据在生成的 JSON 中传送,也可以选择以 CSV 和 XLSX 文件的形式输出。表格也以 PNG 图像的形式输出,允许对表格数据进行视觉验证。
- “figures”文件夹:标识为图形或图像的对象被提取为 PNG 文件。
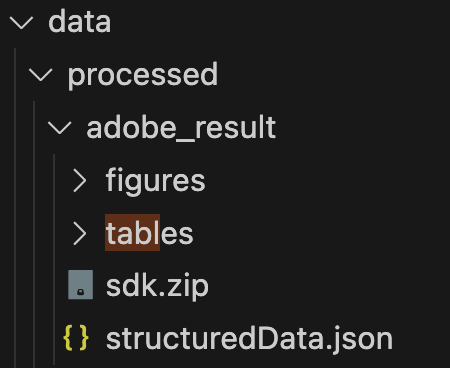
输出文件夹的结构
现在,您可以在文档上应用该功能:
# Adobe output zip file path
input_pdf = 'data/raw/GPTsareGPTs.pdf'
output_zip_path = 'data/processed/adobe_result/sdk.zip'
output_zipextract_folder = 'data/processed/adobe_result/'
# Run adobe API
adobeLoader(input_pdf, output_zip_path)
您可以看到“figures”文件夹以.png格式返回我的 PDF 文档中的所有图像。tables 文件夹返回表格的 Excel 工作表,确保高保真度和准确性,以及用于视觉比较目的的.png图像:

您还可以进一步处理结构化的 JSON 文件以收集文本和表格,并将这些数据组织到 pandas DataFrame 中,以便执行进一步的下游任务:structuredData.json
使用 Camelot 和表格提取表
Tabula 和 Camelot 是两个专为从 PDF 中提取表格而设计的 Python 库。
以下脚本使用 Tabula 或 Camelot 处理 PDF 文档,将文档中的每个表转换为 JSON 格式,同时捕获实际表数据和元数据(如表号和页码):
def extract_tables(file_path, pages="all", package="tabula"):
if package == "camelot":
# Extract tables with camelot
# flavor could be 'stream' or 'lattice', for documents where tables do not have clear borders, the stream flavor is generally more appropriate.
tables = camelot.read_pdf(file_path, pages=pages, flavor="stream")
else:
tables = tabula.read_pdf(file_path, pages=pages, stream=True, silent=True)
# Convert tables to JSON
tables_json = []
for idx, table in enumerate(tables):
if package == "camelot":
page_number = table.parsing_report["page"]
data = table.df.to_json(orient="records")
else:
page_number = ""
data = table.to_json(orient="records")
data = {
"table_number": idx,
"page_number": page_number,
"data": data,
}
tables_json.append(data)
return tables_json
伟大!现在我们有了处理表格的脚本,我们可以将该函数应用于同一个 Pdf 文档:
file_path = '../data/raw/GPTsareGPTs.pdf'
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path)
df_file = pd.DataFrame()
print(f"{datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')} process {file_name}")
print(f"{datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')} extract table")
all_tables = []
for package in ["camelot", "tabula"]:
print(f"{datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')} extract table with {package}")
try:
tables_from_package = extract_tables(file_path, pages="all", package=package) # list of json
for table in tables_from_package:
all_tables.append({"table": table, "source": package})
except Exception as e:
print("----Error: cannot extract table")
print(f"----error: {e}")
# Now you can access each table along with its source
for entry in all_tables:
print(f"Source: {entry['source']}, Table: {entry['table']}")
以下是源 PDF 文档中的表格示例:
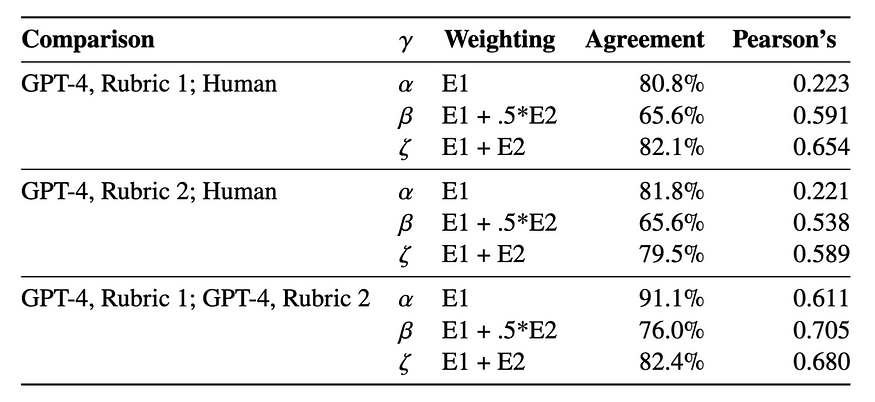
Camelot 或 Tabula 操作的输出格式实际上是表的字符串表示形式,如下面的 json 对象所示:
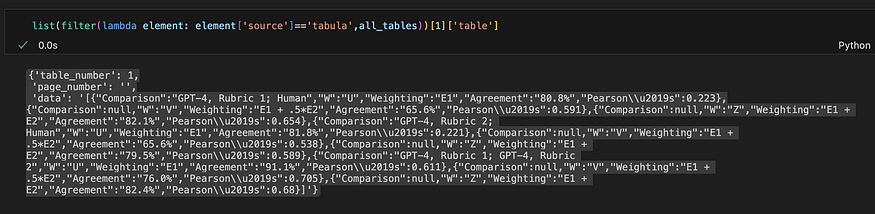
Tabula的输出
当您对 json 对象中的 ['data'] 键进行切片时,VS Code 似乎理解它是一种表格格式,并显示字符串的表格表示形式,看起来与 PDF 文件中的源表完全相同。Tabula 似乎正确检测到该表。棒!
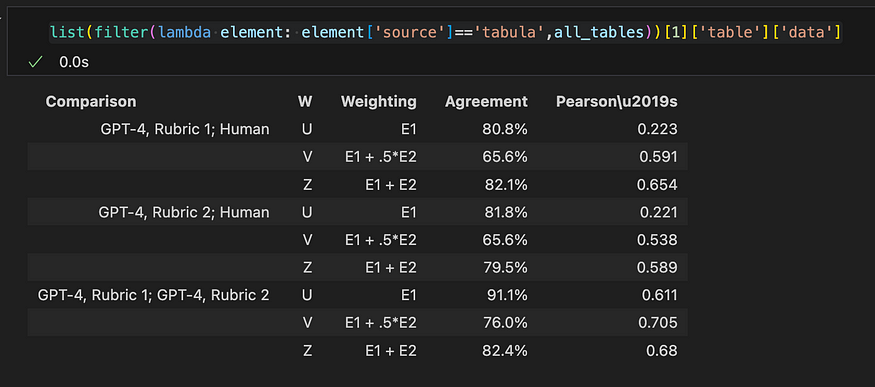
Tabula的输出
现在,让我们看一下 Camelot 的输出。下面显示了同一表的 json 对象。
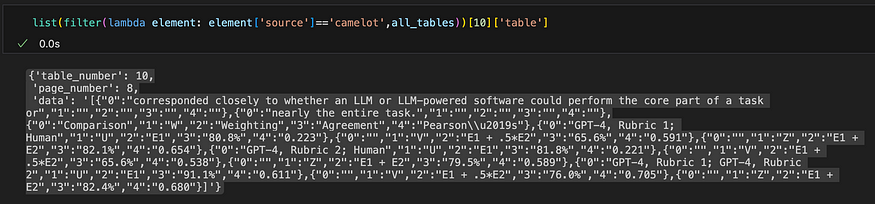
Camelot的产量
以及字符串的表表示:
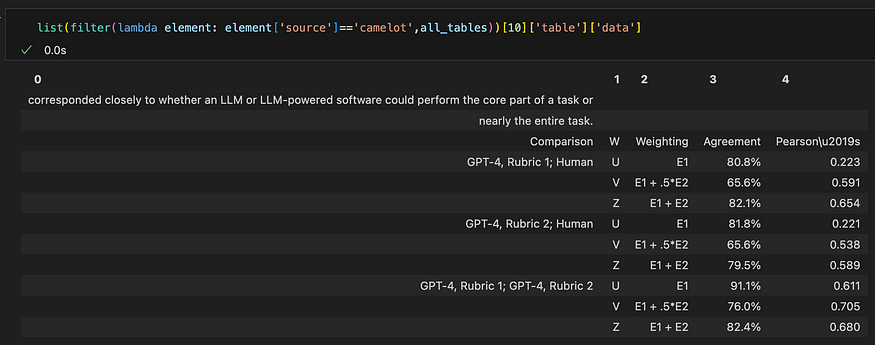
Camelot的输出。Camelot 无法检测到表的边框。当文本离表格太近时,它包括文本。
在此示例中,Tabula 和 Camelot 都能够检测到该表,但是 Tabular 的输出是干净的,并且镜像了 PDF 中的原始表。与此同时,卡米洛特似乎未能检测到桌子的边界。当文本离表格太近时,它包括文本。
但是,在另一个示例中,当页面上存在多个表时,并且没有明确的表边框,如下所示:
Camelot 成功检测了两个表,而 Tabula 无法检测其中任何一个:
Camelot 的输出
Camelot 的输出
不同工具的比较
在考虑选择哪些选项来解析 PDF 文档时,PyPDF 非常适合表格结构可能不是优先事项的基本提取需求。它是完全免费的,适合预算紧张的用户,他们需要一个简单、高精度的文本和图像提取解决方案。根据我的经验,大多数时候,将表格保留为文本的格式是可以接受的。
Camelot 和 Tabula 专门用于表提取,最适合需要表数据提取的场景。它们也是完全免费的,在我看来,如果您对偶尔的不准确感到满意,那就足够了。
Adobe PDF Services API 为文本、表格和图像提取的高精度至关重要的企业或应用程序提供了非常强大的解决方案。但是,没有关于 API 定价的明确信息。在这里,它说您需要联系销售人员以获取报价。在这个线程上,Adobe Extract API 似乎相当昂贵。实际上,我愿意为实际使用付费,因为提取的输出质量很高!
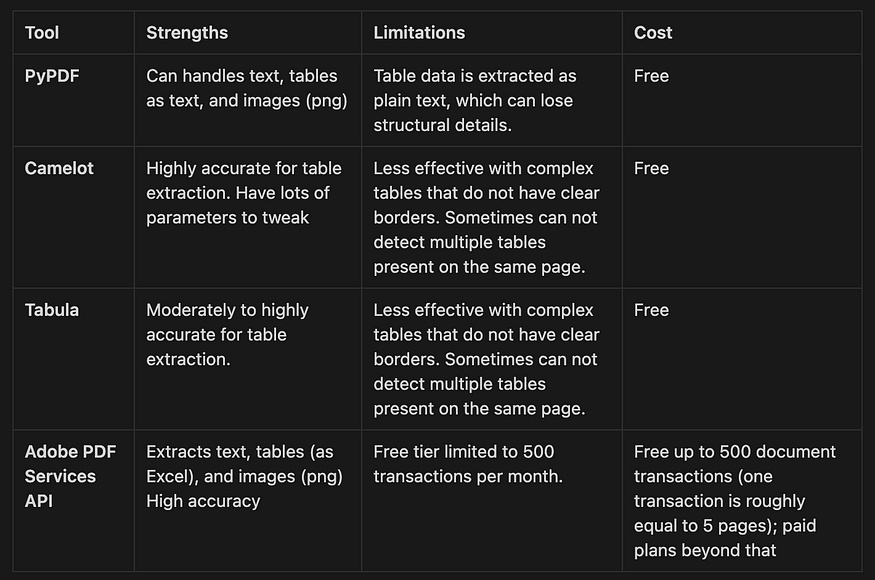
在本文中,我们学习了四种不同的工具,用于解析 PDF 文档以及从 PDF 文件中提取文本、表格和图像数据:PyPDF、Camelot、Tabula 和 Adobe PDF Services API。